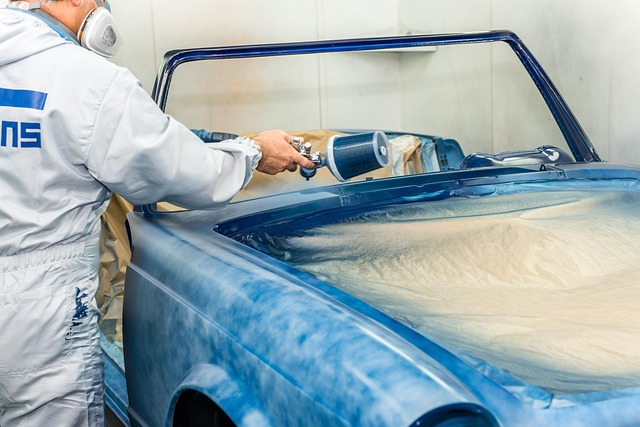
Mastering paint blending techniques is vital for achieving precise color matches and visual harmony in auto bodywork repair. This involves understanding color theory, including primary, secondary, tertiary colors, and complementary hues, to create smooth transitions. Skilled technicians consider color temperature and mix paints meticulously with tools like brushes or sandpaper, transforming collision repairs into seamless reintegrations of original aesthetic appeal. Color wheels are indispensable tools for achieving harmonious blends through complementary and analogous color combinations, suitable for various surfaces including vehicle bodies.
“Unleash your inner artist with our guide to paint blending techniques that masterfully achieve seamless color matches. Dive into the world where complementary and analogous colors dance on your palette, guided by the spin of a color wheel. Learn the art of subtle dry brushing, dramatic wet-on-wet blends, and intricate stippling for textures that sing. Discover tools from brushes to palette knives, along with workspace tips, ensuring consistent, stunning results. Elevate your paint job to a paint blending symphony.”
- Understanding Color Theory for Seamless Blends
- – The role of complementary and analogous colors
- – How to use color wheels for mix creation
Understanding Color Theory for Seamless Blends

Mastering paint blending techniques requires a solid grasp of color theory, which is essential for achieving seamless color matches in auto bodywork or collision repair services. Understanding how colors interact and mix is key to creating smooth transitions between different areas of a vehicle’s surface. This involves recognizing primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, as well as the concept of complementary colors, which can help neutralize or alter other hues.
When applying paint blending techniques, professionals consider color temperature—whether a shade leans towards cool (blue or green undertones) or warm (red or yellow undertones)—to ensure coherent visual harmony. By carefully mixing paints and using specific tools like brushes or sandpaper, skilled technicians can blend colors together, minimizing the visibility of lines or seams. This meticulous approach transforms repairs in collision repair shops from mere fixes into seamless re integrations, restoring the vehicle’s original aesthetic appeal.
– The role of complementary and analogous colors

In the realm of paint blending techniques, understanding color theory is paramount to achieving seamless matches. Complementary and analogous colors play a pivotal role in this process. Complementary colors, like blues and oranges or greens and reds, when mixed together, cancel each other out, resulting in a neutral gray. This property allows them to neutralize one another during the blending process, ensuring smooth transitions between hues. By carefully applying these complementary shades, professionals can create a uniform color across surfaces—a skill essential for projects ranging from meticulous car restoration to precise auto frame repair.
Analogous colors, on the other hand, are adjacent on the color wheel and offer a harmonious blend. When incorporated into paint blending techniques, analogous hues tend to complement each other, creating a visually appealing and cohesive effect. This technique is particularly useful in automotive applications, where achieving a consistent finish is crucial. Whether it’s a vibrant new coat or a meticulous touch-up, understanding how complementary and analogous colors interact enables auto repair shops to deliver top-notch results, transforming a damaged car into a seamless work of color artistry.
– How to use color wheels for mix creation

Color wheels are a powerful tool for artists and painters looking to achieve seamless color matches when using paint blending techniques. By understanding the relationships between colors on the wheel, you can mix hues that complement each other, creating harmonious blends. For instance, if you’re aiming for a neutral tone, mixing equal parts of red, blue, and yellow from the primary colors will yield brown. This method is applicable not only to canvas but also to surfaces like vehicle bodies in car paint services and body shop repairs, ensuring precise color accuracy.
When blending, consider the color wheel’s primary, secondary, and tertiary hues. For example, mixing complementary colors—like blue and orange—can create a rich, vibrant effect. Alternatively, combining analogous shades—colors next to each other on the wheel—results in softer, more subtle transitions, ideal for creating uniform finishes in vehicle body repair work or any other precision painting task.
Mastering paint blending techniques allows artists to create seamless color matches, enhancing their ability to mix perfect shades. By understanding color theory and utilizing tools like complementary and analogous colors, along with color wheels, one can achieve harmonious blends that elevate any painting project. These techniques are essential for achieving professional results, ensuring that every stroke contributes to a cohesive and visually appealing artwork.